-Illustration 1-
Page Template
Page Specification
Page Class
Application Specification
web.xml
In order to understand what makes a JWC and see how the separation of technologies is achieved, among other things, let's open up the "black box" and take a peek at the internals of the JWC. Each JWC is typically made of three parts – an HTML template, an XML specification and one or more Java classes, although a simple JWC can be made by providing just the template. In this illustration let's use all three parts (a purist's approach) to show its industrial strength and then we'll see how it can be simplified for the casual developer, in our next illustration.
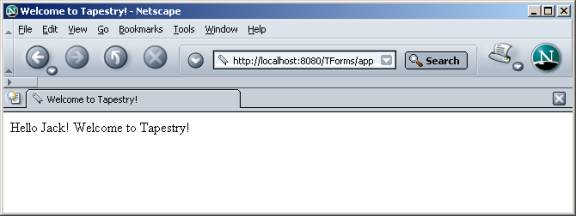
For the purpose of illustration, let's consider a simple one-page Tapestry application that greets the user as shown below.
Figure 1. Home.java
Now that we know a page is also a JWC (specialized), let's build the Page component (Home Page in our example) of our Welcome application using the core library components readily available.
| << Previous | Next >> |